운동하는 공대생
[Computer Vision] CV image overlap(cv2, PIL, image overlap,이미지 연산, 이미지 합성) 본문
Deep Learning/Computer Vision
[Computer Vision] CV image overlap(cv2, PIL, image overlap,이미지 연산, 이미지 합성)
운동하는 공대생 2024. 7. 16. 14:40728x90
반응형
(논문을 작성하는 과정에서 개인적으로 시간이 많이 걸린 부분인데 이것을 정리하기 위해서 작성하였습니다.)
아래의 두 개의 이미지는 Imagenet data에서 가지고 온 사진이다.
여기서 두개의두 개의 이미지 데이터를 활용하여 segmentation 분야에서 두 개의 이미지를 겹치게 이미지를 편집하는 방법을 하고 싶었다.
- image ( 원본 이미지)


- mask ( segmentation의 mask)
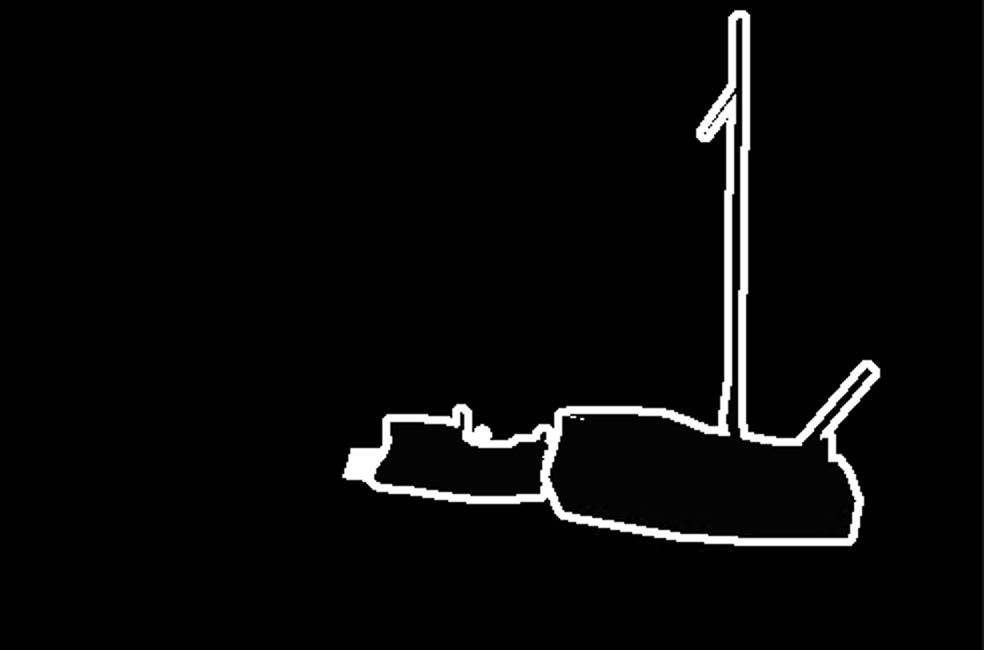
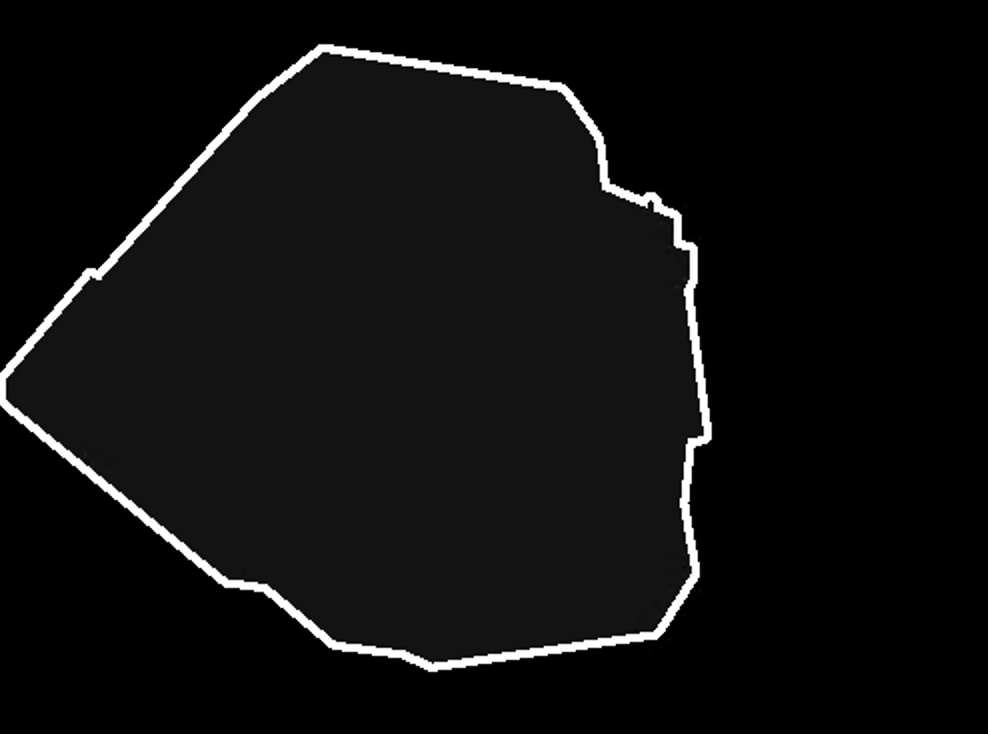
결과
이렇게 두 개의 이미지를 겹쳐서 cv에서 모델이 얼마나 경확도를 유지하는지를 보고 싶었다.
퍼센트를 설정값으로 겹치는 정도를 나타냈으며 0~1 사이의 값을 설정하고 1이 완전히 겹치는 상황을 가정하였다.
- 0.7 퍼센트
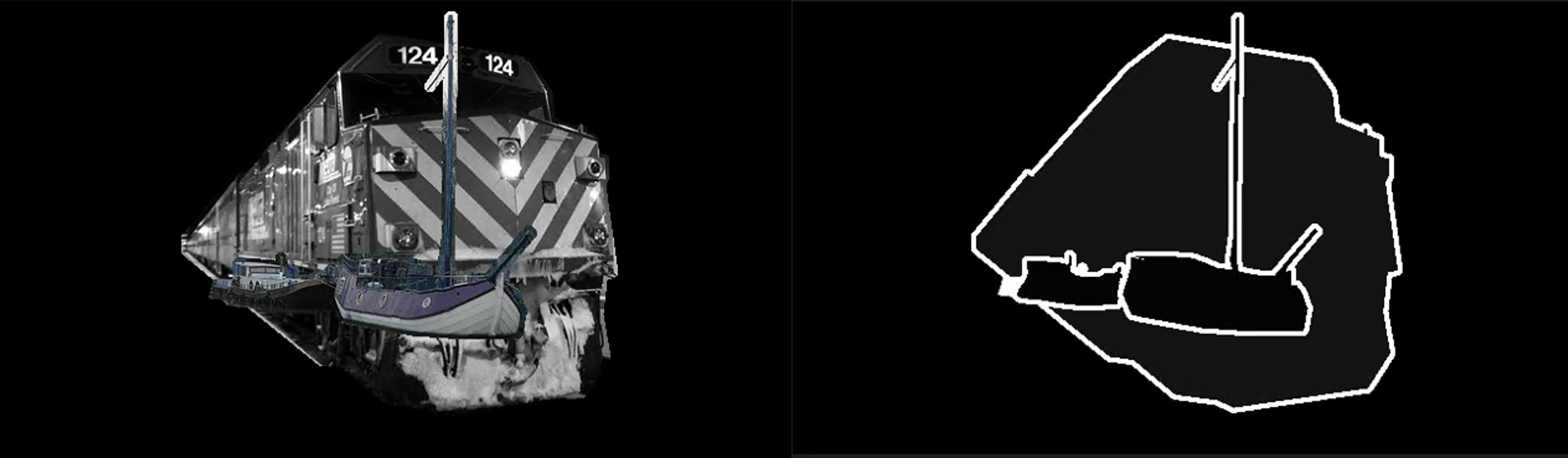
- 0.4 퍼센트

코드
def find_contours(self, mask):
mask_array = np.array(mask)
_, binary_mask = cv2.threshold(mask_array, 128, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(binary_mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
return contours
def extract_inner_region(self, image, contour):
mask = np.zeros_like(image)
cv2.drawContours(mask, [contour], -1, (255, 255, 255), thickness=cv2.FILLED)
result = cv2.bitwise_and(image, mask)
return result
def overlap(self, image, mask, next_image, next_mask, overlap_percentage=0.5):
numpy_image = np.array(image)
original_opencv_image = cv2.cvtColor(numpy_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
next_numpy_image = np.array(next_image)
next_original_opencv_image = cv2.cvtColor(next_numpy_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
contour1 = self.find_contours(mask)
if len(contour1) != 1:
return None,None # If contours are not exactly one, skip processing
inner_region1 = self.extract_inner_region(original_opencv_image, contour1[0])
inner_image1 = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(inner_region1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
contour2 = self.find_contours(next_mask)
if len(contour2) != 1:
return None,None # If contours are not exactly one, skip processing
inner_region2 = self.extract_inner_region(next_original_opencv_image, contour2[0])
inner_image2 = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(inner_region2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
inner_image1_np = np.array(inner_image1)
inner_image2_np = np.array(inner_image2)
inner_mask1_np = np.array(mask)
inner_mask2_np = np.array(next_mask)
# Calculate overlap width
overlap_width = int(inner_image1_np.shape[1] * overlap_percentage)
# Create a canvas to overlay both images
canvas_width = inner_image1_np.shape[1] + inner_image2_np.shape[1] - overlap_width
canvas_height = max(inner_image1_np.shape[0], inner_image2_np.shape[0])
canvas_image = np.zeros((canvas_height, canvas_width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
canvas_mask = np.zeros((canvas_height, canvas_width), dtype=np.uint8)
# Place the first image and mask on the canvas
canvas_image[:inner_image1_np.shape[0], :inner_image1_np.shape[1]] = inner_image1_np
canvas_mask[:inner_mask1_np.shape[0], :inner_mask1_np.shape[1]] = inner_mask1_np
# Overlay the second image and mask on the canvas with overlap
start_x = inner_image1_np.shape[1] - overlap_width
for i in range(inner_image2_np.shape[0]):
for j in range(inner_image2_np.shape[1]):
if canvas_mask[i, start_x + j] == 0:
canvas_image[i, start_x + j] = inner_image2_np[i, j]
canvas_mask[i, start_x + j] = inner_mask2_np[i, j]
# Convert the canvas back to an image and mask
result_image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(canvas_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
result_mask = Image.fromarray(canvas_mask)
return result_image, result_mask
코드 설명
- overlap 함수에서는 PIL 이미지 형식으로 데이터를 받아온다.
- mask를 기준으로 각각 물체를 추출한다( find_contours : 물체의 기준선을 찾아준다. , extract_inner_region : 이미지에서 mask의 안쪽 부분만 추출한다.)
- 이제 두 개의 추출된 이미지 (inner_mask1, inner_mask2)를 활용하여서 numpy 형식으로 변환하여 겹치는 부분을 측정하고 서로 기준이 되는 이미지에서 픽셀값이 0인 부분(배경) 은 겹치는 부분의 데이터가 침범이 가능하도록 코드를 작성하였다.
728x90
반응형
'Deep Learning > Computer Vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Computer Vision] 컴퓨터 비전과 딥러닝 5장- 호모그래피 추정 (0) | 2023.07.28 |
|---|---|
| [Computer Vision] 컴퓨터 비전과 딥러닝 5장- 매칭 (0) | 2023.07.22 |
| [Computer Vision] 컴퓨터 비전과 딥러닝 4장- 대화식 분할, 영역 특징 (0) | 2023.07.14 |
| [Computer Vision] 컴퓨터 비전과 딥러닝 4장- 영역 분할 (0) | 2023.07.14 |
| [Computer Vision] 컴퓨터 비전과 딥러닝 4장- 캐니 에지 (0) | 2023.07.13 |




